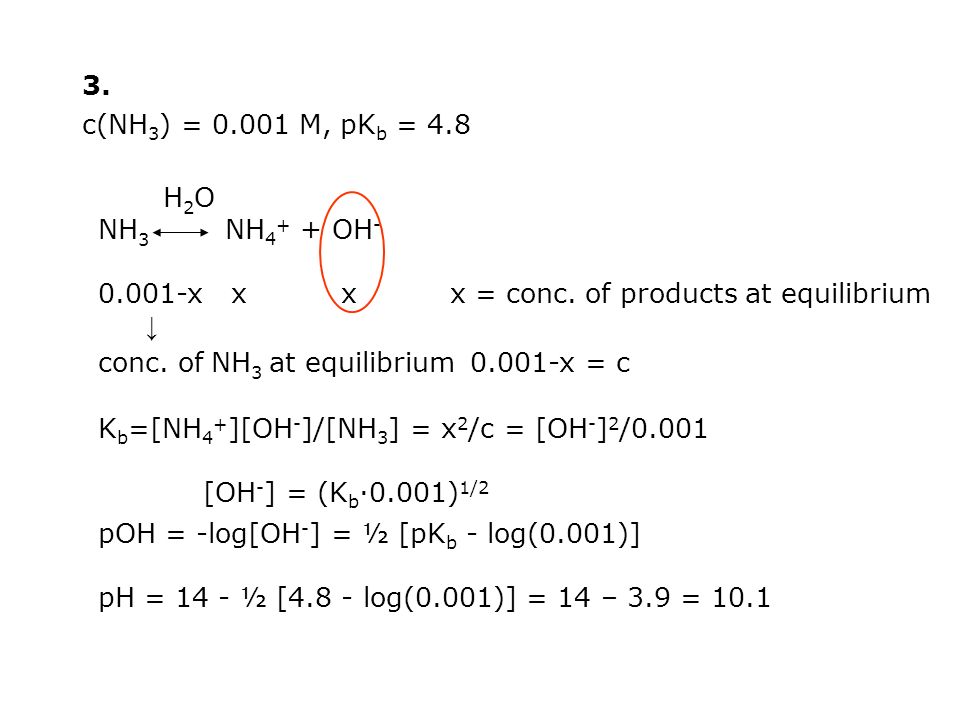![How is pH = 1/2[pKa - logc] - Chemistry - Chemical and Ionic Equilibrium - 13113047 | Meritnation.com How is pH = 1/2[pKa - logc] - Chemistry - Chemical and Ionic Equilibrium - 13113047 | Meritnation.com](https://s3mn.mnimgs.com/img/shared/ck-files/ck_57fe3e2aeb864.png)
How is pH = 1/2[pKa - logc] - Chemistry - Chemical and Ionic Equilibrium - 13113047 | Meritnation.com

PPT - 2- Weak acid - Strong base titration :- eg. CH 3 COOH (pKa = 4.74) and NaOH PowerPoint Presentation - ID:2976551

Match the List - I (solution of salts) with List - II (pH of the solution) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:List - IList - IIA.

PPT - Calculations involving acidic, basic and buffer solutions PowerPoint Presentation - ID:3259307
Page 1 of 7 Chem 201 Lecture11 Summer'07 Admin: recall all Test #1's Please turn in Test 1 for regrading Last time: 1. calib

pH of a solution of salt of weak acid and weak base is : pH=1/2pKw+1/2pKa-1/2pKb and that of weak acid and strong base is pH=1/2pKw+1/2pKa+1/2logc pH of 0.1 M solution of ammonium
1 a) first start with the forms of asp: pKa's: 2.0 3.9 10.0 H3A+ <====>H2A<====> HA-<=======>A2- 12.0

Match the List - I (solution of salts) with List - II (pH of the solution) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:List - IList - IIA.
![When a salt reacts with water to form acidic or basic solution, the process is called hydrolysis. The pH of salt solution can be calculated using the following reactions: pH=1/2[pKw+pKa +log C] When a salt reacts with water to form acidic or basic solution, the process is called hydrolysis. The pH of salt solution can be calculated using the following reactions: pH=1/2[pKw+pKa +log C]](https://d10lpgp6xz60nq.cloudfront.net/question-thumbnail/en_643839541.png)
When a salt reacts with water to form acidic or basic solution, the process is called hydrolysis. The pH of salt solution can be calculated using the following reactions: pH=1/2[pKw+pKa +log C]
![SOLVED: Equations: pH = pKa log ([b] /[a] (Ka) (Kb) = 1x 10-14 Kb = x2/ (y-x) K = xl/ly x) pH (pKa1 pKa2)/2 pK,'s of amino acid side chains: D (3.9), SOLVED: Equations: pH = pKa log ([b] /[a] (Ka) (Kb) = 1x 10-14 Kb = x2/ (y-x) K = xl/ly x) pH (pKa1 pKa2)/2 pK,'s of amino acid side chains: D (3.9),](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/2531a2f0c6754ab3ba0caf17c487c22e.jpg)